Bio-Diesel
Pre-treatment of waste cooking oils.( WCO) waste cooking oils (WCO) which contain large amounts of free fatty acids produced in the restaurants, are collected by environment protection agency.
A two step catalysed process is adopted to prepare Biodiesel from WCO whose acid value is 72.92 +/- 0.036 Mgk /g.
The free fatty acids of WCO were esterified with methanol , catalysed by ferric sulfate ( Fe2 ( So4)3] in the first step and the triglycerides ( TGS) in WCO were trans-esterified with menthol catalysed by potassium hydroxide in the second step.
Ferric sulfate had high activity to catalysed the esterification of free acids with menthanol. The conversion reate of FFA reaches 97.22% when 2% by weight of Ferric Sulphate is added to the reaction system containing methanol to TG in 10:1 ( mole ratio) composition & reaches at 95 degaree C in 4 hours. The Methanol is vacuum evaporated & the transesterification of the remained triglyceride is performed at 65 degree C for 1 hours in a reaction system containing 1 WT % of potassium hydroxide and 6:1 mole ratio of methanol to TGS.
The final product with 97.02% of Biodiesel, obtained at two the step catalysed process it is found that this new process has many advantages compared with the old process such as no acid , waste water, high efficiency, low equipment cost & easy recovery of catalyst.
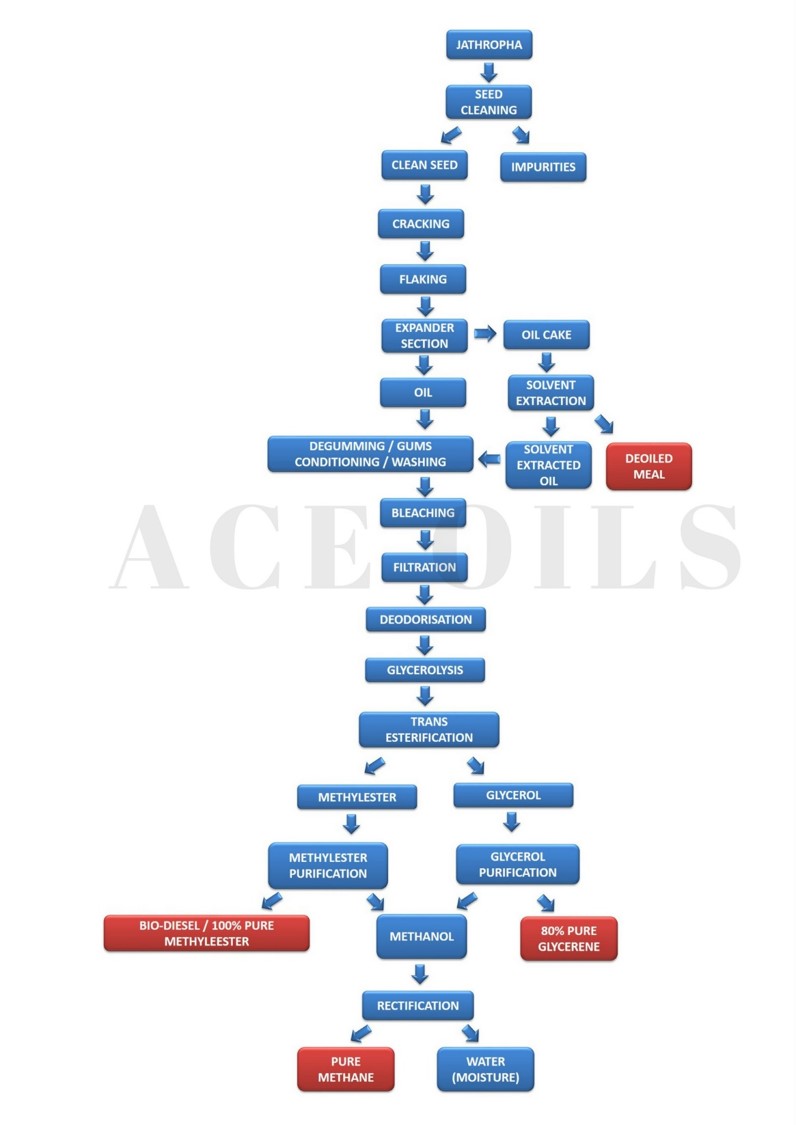
TRANSESTERIFICATION & METHYL ESTER PURIFICATION
PROCESS DESCRIPTION
The plant consists basically of one batch reactor and some peripheral items such as a special catalyst introducing system and a catalyst / oil mixer, the pumps and vacuum unit. The proposed post – treatment is designed on a dry basis.
METHYLATION
The Refined oil (moisture < 0.01% F.F.A. < 0.05%, very low PV) with 13% methyl alcohol is pumped rapidly into the reactor through a heater, to heat the oil by low – pressure steam till approximately 1100 – 1200C.
When the oil acidity is above 0.1% FFA, the oil is contacted with caustic soda in a mixer, in order to eliminate as much as possible the fatty acids, considered as a poison for the catalyst. A dosing unit, feeds the caustic soda solution.
The oil is sprayed in the reactor vessel with heating and cooling coil, agitatation. The reactor operates under vacuum obtained by the condenser vacuum unit. To continue the oil drying, the oil will then be re-circulated by pump and at the same time, the main vacuum unit increases the vacuum till about 10 mbar.
When the oil is dried, the catalyst is introduced. The catalyst being very sensitive to moisture of the ambient air, it has to be introduced in an appropriate way. The bag will be opened in a restricted volume. Preferably under depressure or nitrogen blanketing. The dosing system will perform this job under the best conditions for the operator, as the catalyst is also a bit aggressive to eyes and skin. The catalyst is then introduced in the oil by the circulating pump.
Methylation reaction usually takes a short time of maximum half an hour.
When reaction occurs, the oil colour changes : the oil becomes darker. This can be seen through the re-circulation sight glass or by taking a sample. The product so obtained is pumped by pump to a settling tank. Here the solids at 1% are settled and decanted.
The clear liquid is then sent through pump and shell and tube steam heater (from 400c to 600c) to the second reactor where final methylation taken place. The product so obtained is pumped by pump to the 2nd settling tank where glycerine is separated by settlement and Methy Ester + 4% alcohol proceeds through pump to expansion vessel and then through a steam heater to cyclone separator where methyanol vapour are separated (subsequently converted to liquid form though water cooler) The methyl ester with traces of soapy water is cooled in Cooler and then sent to centrifuge to separate soap stock and pure methyl ester is then pumped to neutraliser where PH is controlled by addition of HCL.
The product so obtained is Methyl Ester or Bio-diesel.
GLYCERINE PURIFICATION AND CONCENTRATION
Raw Glycerine Purification – Soap Splitting
The purpose of the treatment is the acidification of the raw glycerine stream, so to neutralize the residual catalyst and to split the soaps formed during transesterification. Subsequently, the fatty acid derived form soap splitting are separated and the pH of the purified glycerine, is finally adjusted.
The raw glycerine stream coming from the feeding pump is sent to the flash drum to separate the methanol previous an heating step by means of the heat exchanger.
The methanol evaporated in the flash drum is sent to methanol rectification unit.
The gycerine coming from the flash drum is sent, by means of the transfer pump to the static mixer, where is mixed with Hydrochloric Acid.
The acidified steam is fed to the split reactor equipped with an external recycle through the pump. The quantity of hydrochloric acid is controlled with an automatic pH controller with the aim to guarantee a pH lower than 5 inside the reactor.
From the recycle delivery line of the pump the mixture glycerine/fatty acid is sent under level control to the separator.
The stream of glycerine separated from fatty acid (containing methanol and water), is fed to the neutralizing vessel where the pH is adjusted o the neutrality value by addition caustic soda solution 50%.
The fatty acid stream coming from the top of the separator is recycled to the esterification by means of the feeding pump or to Battery Limits in case of no installation of the Esterification Unit.
The neutralized glycerine stream coming from soaps splitting section is sent to the methanol flash distillation circuit consisting of the following equipment:
- Glycerine Heater
- Glycerine Feeding Pump
- Glycerine Transfer Pump
The glycerine stream is sent to the recovery pre-heater by means of feeding pump sent to the vapor heater before going to the flash drum.
The purified and concentrated outgoing glycerine is transferred under control level through the pump to storage.